Embarking on the journey to create a comprehensive IT strategy can be a daunting yet crucial endeavor for modern businesses; in this insightful guide, we provide you with essential tips, examples, and best practices to help you design and execute an effective IT plan that propels your organization toward success.
Information technology (IT) is playing an increasingly important role in modern business, given the rising advances in technology and the growing reliance on digital solutions for operation and competition. Whether it's storing, processing and analyzing data, automating administrative tasks or just the typical use of tech in the workplace, it's becoming increasingly central. Unfortunately, not all businesses are maximizing these advantages. What could be the reason?
The 10+ years of working in this industry has given us the incredible chance to interact with many organizations from various sectors, and this opportunity has helped us understand why many companies are struggling with IT. Surprisingly, it mostly boils down to develop and follow an IT strategic plan. Many CIOs and IT departments fail to realize that even with enough resources to deploy whatever technology you want, it could still fail if you ignore planning.
So this guide dives into IT Strategic Planning, providing you with all the ingredients you need to put together a winning IT Strategy Plan.
Also Read: Common IT problems
What is an IT strategic plan?
An IT strategy plan is the comprehensive document that serves as a roadmap for the IT strategy, outlining how an organization will use technology to achieve its goals. It defines the specific actions and initiatives that will be undertaken to align the organization's IT efforts with its overall mission, business strategy, and priorities. There are serious risks that come with neglecting to integrate IT planning into your business strategy.
A good IT strategy should align with the overall business strategy and goals of the organization. It should also take into account the current state of the organization's technology, the organization's budget and resources, as well as regulatory or compliance requirements.
The strategy should be flexible enough to adjust according to any new organizational demands, business objectives, external trends, available expertise, or user requirements. For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic forced many organizations to update their strategies.
Who creates the IT strategic plan?
Ideally, the CIO, or Chief Information Officer, is typically responsible for leading the development and implementation of the plan.
However, even in the absence of a CIO, it's still possible to develop an effective IT strategy. In such cases, the IT team, whether it is internal or outsourced, takes on a more prominent role in leading the process. This is particularly the case for SMBs, as they often have limited resources and budget to recruit a CIO or CTO.
Also Read: CTO as a Service: a Full Guide
Questions the IT strategic plan should address:
- What resources do we need both internally and externally?
- What technology investments are necessary to reach the business goals?
- How will success be defined and evaluated?
- How will the organization's IT strategy evolve over time to meet the changing needs of the business?
- What IT initiatives and projects should be undertaken in the short-term and long-term?
Benefits of IT strategic plan
As we've already seen, the IT strategy plays the key role of aligning the organization's technology investments with its business goals, which can lead to a range of benefits. Here are the top ones:
1. Increased security
The right IT strategy can contribute to increased security by ensuring that your organization has the necessary safeguards in place to protect against threats. Here are two examples:
- Risk assessment and management: The IT strategy document can guide the security teams to identify and assess potential security risks, as well as provide a roadmap for how to mitigate those risks. This might include measures such as implementing strong password policies and regularly updating software to fix vulnerabilities.
- Investment in security infrastructure: An IT strategy can also provide guidance on the types of security measures and technologies that an organization should invest in. This might include investing infirewalls, VPNs, intrusion detection systems, SIEM tools, SOAR tools and other security solutions to protect against cyber threats.
Developing an IT strategy can help you come up with solutions to any gaps in your network security. With it, you can easily outline the current state of various items, which can be very insightful information on how to minimize attack vectors.
Also Read:
2. Change management
Change management is a critical component of the strategic IT plan as it ensures that the organization is prepared to respond to changes in the industry, technology, and market trends.
The goal is to make the transition to the new way of doing things as smooth as possible, while minimizing disruption.
Here are some ways a great IT strategy can help with change management:
- Planning for change: Since the strategic IT plan provides a structured approach to change management, it means that organizations have a better way to anticipate changes, and implement them the right way.
- Prioritization: A great IT strategy can help to prioritize changes based on the organization's goals and objectives.
- Communication: A well-constructed IT strategy provides clear channels of communication. This makes it easy to educate and support stakeholders and employees throughout the change process, which leads to better acceptance of the changes.
Example: A company wants to move its financial reporting system to the cloud in order to improve efficiency and reduce IT costs. The IT strategy plan outlines the steps that will be taken to migrate the system to the cloud. These steps might include the selection of a cloud provider, the testing and validation of the new system, and the training of employees on how to use the new system. This roadmap helps ensure that the cloud migration is managed effectively and that any potential issues are addressed in a timely manner.
3. Cost management
IT spending can quickly get out of hand if not planned, and there is no better tool to help you prevent this than the IT strategic plan. It comes in handy when you want to identify and assess the costs associated with different technology options. This will then inform decision-making around which solutions to invest in, and which can wait.
Most importantly, the plan can help identify opportunities for cost savings. For example, the strategy might recommend using open-source software or cloud-based solutions to reduce software licensing costs, or might suggest consolidation of certain aspects of the IT infrastructure to reduce maintenance and management costs.
4. Improved decision-making
The IT strategy document offers a structure for assessing and contrasting various technological solutions, simplifying the process of making strategic decisions regarding technology investments.
Imagine that a company is considering implementing a new customer relationship management (CRM) system. The IT strategy includes a section on CRM systems, which outlines the benefits and potential drawbacks of different options. It also includes criteria for evaluating different CRM systems, such as their scalability, integration with other systems, and user-friendliness.
Using this information, the company can assess the costs and benefits of different CRM systems, and can make an informed decision about which system is the best fit for its needs. The plan can also provide guidance on how to roll out a new CRM system, including a timeline, budget, and resource requirement.
5. Agility
The ability to quickly adapt the technology infrastructure to changing business needs is key for any organization, and this is one area that your IT strategy plan will prove incredibly useful. It simply provides a structured approach for making changes, and this means you can more readily respond to new opportunities and challenges.
Let's say you are an e-commerce company that is seeing an increase in demand for a particular line of products, and you need to quickly expand your platform to accommodate this growth. Your IT strategy includes a section on e-commerce infrastructure, which outlines the various options for scaling the platform, including adding new servers, implementing a content delivery network (CDN), and optimizing the website for performance.
With this ready-to-go structure, you are able to assess the costs and benefits of different options, and choose the approach that is most appropriate for this need.
6. Enhanced vendor management
Having an IT strategy in place can enable an organization to secure more advantageous terms from technology vendors, as well as a framework for assessing vendor performance.
With already established goals, you have the upper hand when negotiating with vendors. You know what your needs are, and don't have to take advice from the vendor just because they assert it's best for you. That being said, the vendor can still guide you in some areas if you'd like. Additionally, having a clear understanding of your needs allows you to communicate them effectively to vendors, giving you an advantage when dealing with them.
Vendor performance is also a major factor in vendor management. The strategy enables us to assess how vendors are doing against the predetermined goals and objectives for technology utilization within the company. The best part is that you can actually use this performance data to leverage better pricing or other concessions from vendors.
7. Compliance
We're living in the compliance era, which means some of your tech needs to meet industry and government regulations. Your strategy will make it easier by giving a structure for things like regular reviews and audits. Instead of having teams continually chasing after compliance standards, just include it in your IT strategy. This way, all departments will stay updated as the requirements keep changing.
Two of the most well-known compliance standards are the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Your strategy should include the steps to comply with these standards. Furthermore, in the event of any modifications or changes, you can simply refer back to your strategy and make the necessary adjustments.
Also Read:
- What is SOC2? Everything You Need to Know for Compliance and Certification
- PCI DSS Compliance Goals
- MSP HIPAA Compliance Checklist
8. Enhanced talent management
Many organizations struggle to accurately assess their current and future tech needs, as well as the related skills and competencies needed to effectively use it. But with a well-developed IT strategic plan in place, this shouldn't be an issue. The plan will guide you in developing and retaining top talent, including what the best practices for recruiting are.
But to make sure you're covering all your bases, with regard to telnet management, the strategy should take into account the changing skills and competencies required due to changes in technology and emerging trends. This means the IT talent strategy should be updated continuously and not just treated as a one-off project.
9. Sustainability
With the help of a well documented IT strategy, you can easily spot opportunities to employ technology to lower the environmental footprint across your supply chain. This could mean capitalizing on digital platforms and tools to maximize production and logistics, or using data analytics to recognize areas where sustainability can be increased.
Technology such as 3D modeling, digital twins and simulations can help with enhancing product design in order to decrease environmental impact.
What should be included in the IT strategy plan?
Business Objectives | The plan should clearly state the organization's overall business objectives and how information technology will support the achievement of those objectives. |
IT Vision & Mission | The organization's IT vision and mission statements, which should align with the overall business vision and mission. |
Current State Assessment | An assessment of the organization's current IT capabilities, including hardware, software, and processes, as well as an analysis of how well they support the organization's operations. |
Future State Vision | A clear vision of what the organization's IT capabilities should look like in the future in order to best support the business. |
Strategic Initiatives | The plan should identify specific strategic initiatives that will be undertaken to close the gap between the current and future state visions. These initiatives could include projects, programs or process improvements. |
Implementation Plan | A detailed implementation plan outlining the steps that will be taken to execute the strategic initiatives and achieve the future state vision. This should include timelines, milestones, and key performance indicators for measuring progress. |
Risk Management | A risk management strategy that identifies potential risks to the organization's IT operations and outlines how they will be managed. |
Resources | A budget and resource allocation plan, outlining the financial and personnel resources required to implement the plan. |
Monitoring & Review | A process for monitoring and reviewing the progress of the plan, including regular reviews, reports and an evaluation process. |
Please note that the items here are not exhaustive. Feel free to add more or subtract those you feel do not apply to your organization.
5 steps in IT strategy planning
Developing an effective IT strategic plan is a multi-step process that involves key phases. The specific steps and the level of detail in each phase may vary depending on the organization, but here is a general overview of the process.
Step 1: Assessment
The strategy building process begins by evaluating the current state of the organization's IT capabilities, infrastructure, and systems.
These activities are the core of this phase, but feel free to tailor them to your organization's needs
- SWOT Analysis: Identify the organization's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats that relate to the IT capabilities, infrastructure, and systems. This analysis should be conducted by a cross-functional team, including IT staff and other key stakeholders, such as business leaders and customers.
- Interviews: Conduct interviews with key stakeholders to gather information that can complement that obtained from SWOT analysis.
- Data Collection: Collect data from various IT systems, such as databases, servers, networks, and applications. The data collected can include information such as system performance, capacity, availability, and security. You can use this to identify areas of improvement and potential risks.
- Benchmarking: Compare the organization's IT capabilities with those of similar organizations in the same industry or sector. The benchmarking process can be used to identify best practices and areas for improvement.
- Gap analysis: Compare the IT capability to the desired state, cutting across technology, processes, people and organizational structure.
Example: A retail organization might conduct SWOT analysis to identify its IT strengths, such as a highly efficient inventory management system and a well-trained IT staff. Weaknesses might include a lack of mobile optimization on their website and a lack of analytics capabilities. Opportunities might include the potential to expand their online sales, while threats might include increased competition from other retailers.
Be sure to get buy-in from all stakeholders during the assessment phase. This way you are able to identify any potential issues early on, and work to address them before they become major obstacles.
Step 2: Strategy Development
Based on the results of the assessment step, it's now time to develop the IT strategic plan. Key activities for this stage include:
- Identify IT initiatives and projects: What are the IT initiatives and projects that will be undertaken to support the organization's overall goals and objectives. These may include areas such as business process automation, data analytics, digital transformation, cybersecurity, and cloud computing.
- Set objectives and metrics for success: Objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Use metrics to measure progress and evaluate the success of each initiative and project. Also read: Top 25 IT KPIs and Metrics You Should Track
- Funding: Allocate resources and budget for each IT initiative and project. This includes identifying the personnel, equipment, and other resources that will be required, as well as developing a financial plan for each initiative and project.
- Roadmap development: Create a roadmap that provides a high-level overview of what initiatives and projects will be undertaken, when they will be undertaken, and how they will be undertaken.
- Alignment: Ensure that the IT initiatives and projects are properly aligned with the overall business strategy and vision.
- Assign roles: Determine who will be responsible for specific tasks and activities. This includes who will be responsible for specific aspects of the work, and who will be accountable for delivering results.
Example: A healthcare organization's overall goal is to improve patient care by streamlining their appointment scheduling process. The IT strategic plan for this organization might include an IT initiative to develop a patient portal where patients can schedule appointments online. Objectives for this initiative might include increasing the number of appointments scheduled through the patient portal by 20% within the next 12 months. Metrics for success might include the number of appointments scheduled through the portal and patient satisfaction with the scheduling process. Funding could include budget and resources such as hiring a team of developers and designers to create the portal, and integrating it with the organization's existing systems. Alignment may include linking the initiative with overall business strategy and regulatory compliance.
As you can see, this phase involves a lot of critical thinking, data analysis, and decision making, as it's the foundation of the IT strategic plan. If the resources seem inadequate, it is necessary to reevaluate the strategy.
Step 3: Execution
The organization begins to implement the projects and initiatives as outlined in the plan. This may involve procuring new hardware and software, training employees, and rolling out new systems or processes.
The main goal of this phase is to define exactly what are the deliverables and outcomes. This is important as it is closely connected to reaching the business objectives.
Step 4: Review
After the execution phase, the organization evaluates the success of the IT strategic plan by comparing the results to the original goals and objectives. This may involve analyzing metrics such as cost savings, improved productivity, or increased customer satisfaction.
This phase presents the ultimate opportunity for the organization to see where the plan is going and create a feedback loop that can help to increase efficiency.
Step 5: Maintenance and improvement
Based on the results of the review, the organization may identify areas where the plan needs to be tweaked or improved. This may involve continuing to fine-tune and optimize systems, as well as staying up-to-date with new technologies and trends in the industry.
If the IT strategic plan doesn't work as expected, you can change it based on what's been learned throughout the journey. It is important to remember that IT strategic planning is a continuous process that must always be relevant for the organization.
We can also summarize the above steps into four levels that are commonly referred to as the the 4 main points of IT strategic planning, namely:
- Environmental scanning
- Strategy formulation
- Strategy implementation
- Strategy evaluation and maintenance
3 IT strategy examples
There is no stand-alone industry standard for creating an IT strategic plan. As a result there are various processes and examples for strategic planning. Most of them have some common thread between each other, but every single one of them is unique in its own way.
Let's have a look at some examples of IT strategy plans.
IT strategy plan example 1
Source: CMS Technologies
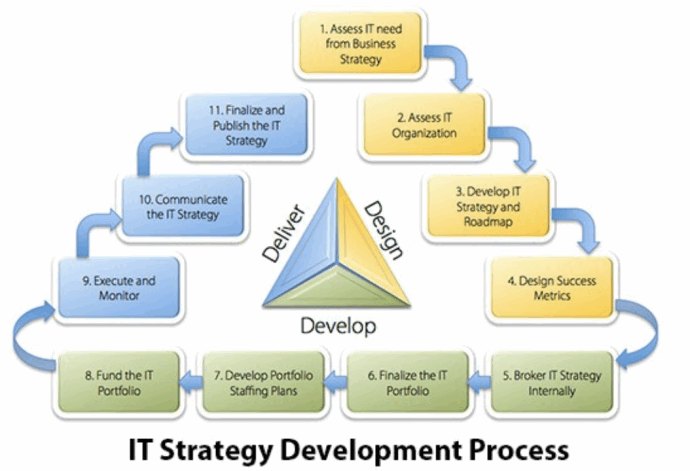
As we can observe from the image, CMS technologies break down IT strategy development into three primary tiers: Design, Develop and Deliver. Each of these are composed of 3-4 procedures to guarantee a comprehensive development of the tactic every step of the way, from analyzing the corporation's assets to how it communicates.
IT strategy plan example 2
Source: CIO Index
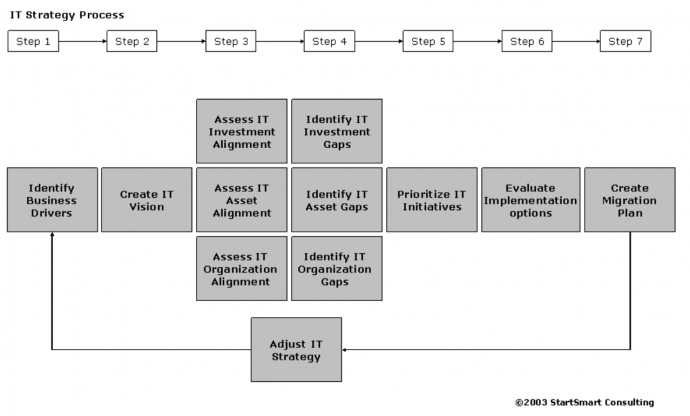
This IT strategy example from CIO Index is a bit more intricate. It's broken down into seven stages, with 1-3 layers beneath each one. The process begins with recognizing business diversities and formulating an IT vision. Lastly, it is time to evaluate and develop a Migration Plan which allows for modification of the IT strategy by forming a loop.
IT strategy plan example 3
Source: Info-Tech Research Group
This IT strategic plan example from the Info-tech research group is a simple yet effective procedure for aligning IT strategy with the organization's initiatives and objectives. The plan is specifically designed for small and medium-sized enterprises.
It includes different sections, such as the purpose of the plan, corporate strategy, business initiatives, IT strategy, and IT strategic plan.
IT strategic plan use cases
The past decades saw most organizations primarily utilizing the strategic IT plan when investing in costly technology. This made perfect sense, as it provided a process around spending big money and helped organizations ensure that they were getting the most value from their technology investments.
However, in recent years, the role of technology has evolved to become more than just buying new hardware and software. Technology has become an integral part of organizational operations, and as such, the strategic IT plan is finding new and diverse use cases, including operational.
Here are the most notable ones;
1. Mergers and acquisitions
A strategic IT plan can prove instrumental in merger and acquisition to ensure a smooth integration of IT systems and processes of the two organizations. It provides the framework for aligning the IT capabilities and goals of both the organizations.
So if company XYZ wants to merge with company ABC, they develop a strategic IT plan to align the IT capabilities and goals of both the organizations, and also identify and eliminate any duplicated systems.
2. Digital Transformation
The key driver behind digital transformation is the need to stay competitive in an increasingly digital world, where customers expect access to information and services 24/7, and where traditional business models are being disrupted by digital-native companies. This need is fueling spending as the market is projected to skyrocket to USD 4.339 trillion by 2030 — up from its current value of USD 752.38 billion in 2023.
So how can a strategic IT plan help your organization to take full advantage of digital transformation? A robust IT strategic plan prioritizes the most important digital transformation initiatives and guides the adoption of new technologies. It also includes a change management plan to ensure a smooth transition with minimal disruptions.
Let's use a quick example of a retail company that wants to shift its business model to an e-commerce platform and mobile application. Their goal is to increase sales and customer engagement. The company can use strategic IT planning to identify key areas of the business that need to be transformed, such as customer experience, inventory management, and supply chain. They can then prioritize and plan the implementation of the necessary technology, such as e-commerce platform, mobile application, and data analytics, to support the transformation.
The plan will also aid in identifying the necessary changes to processes and organizational structure that will support the digital transformation.
3. Workforce technology
A strategic IT plan can guide the organization to provide the tools and resources that employees need to be productive. This may include devices, applications, collaboration tools, and IT training
Let's say a large manufacturing company wants to improve its workforce productivity by providing employees with mobile devices and applications to access information and perform tasks on the go. The company can use a strategic IT plan to identify the specific devices and applications that are needed, determine the best deployment and management strategies, and develop training and support programs for employees.
4. Innovation
A strategic IT plan can help organizations to foster an innovative culture that encourages and supports the development of new ideas, products, and processes. Here are a few ways this can play out:
- Encouraging experimentation: A strategic IT plan can set a framework for experimentation and exploration. This entails giving a direction for setting aside resources and time for experimentation, as well as giving employees a degree of freedom to explore new ideas.
- Supporting collaboration: A strategic IT plan can help organizations to create an environment that fosters collaboration, which could eventually spur innovation.
5. Infrastructure optimization
A strategic IT plan can be used to optimize an organization's IT infrastructure components, including hardware, software, and networks
Depending on needs, you can create a plan that provides a useful guide around aspects such as consolidating servers and data centers, modernizing hardware and software, and implementing virtualization and cloud technologies.
Also Read:
6. Cybersecurity
You can use the strategic IT plan to enhance your organization'ssecurity posture by providing a blueprint upon which the IT teams, whether in-house or outsourced, will easily identify potential threats and implement preventive measures.
For example, a healthcare organization wants to enhance its cybersecurity posture to protect patient data and ensure compliance with regulations such as HIPAA. The company can use their strategic IT plan to identify potential cyber threats and vulnerabilities. The company can then prioritize and develop a plan to implement and manage security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and multi-factor authentication.
Also Read: Rising cyber attacks on Us hospitals
Top IT strategic planning software
These tools are a great asset when it comes to planning, executing and monitoring IT strategies. Although there are plenty of choices available, we've compiled the top ones and present them to you here.
Keto | Ketosoftware offers a strategy and change management toolkit. This toolkit offers features such as hierarchical linking of strategies, objectives and actions; as well as a strategy portfolio view. |
Smartsheet | A project management and collaboration software that allows teams to plan, execute, and track their work in real-time. It also provides tools for strategic planning, including templates. |
Collibra | A data governance software that helps organizations manage and share their data assets. |
Entomo | A performance management software for employees that can help organizations to optimize their IT resources and services. |
Planview | A project and portfolio management software that helps organizations plan, prioritize, and manage their IT initiatives. |
ApptioOne | A solution provided by Apptio that offers an integrated platform to manage IT operations. ApptioOne enables IT leaders to consolidate data and insights from multiple sources and use them to optimize their IT services and resources. It supports IT leaders to make better decisions by providing a real-time view of the IT investments and performance, providing tools to forecast and plan future investments, and identifying areas of cost savings and improvements. |
Hive | A collaboration and project management software that also has features for strategic planning. |
Asana | A project management software that allows teams to plan, execute, and track their work in real-time. One of its products is a tool that is specifically designed for strategic planning, dubbed Asana Goals. |
Cascade Strategy | As the name suggests, this is precisely a software for planning and execution, allowing organizations to map, track and monitor the performance of their business strategy. In the context of IT, IT leaders can use this tool to align IT strategy with business strategy, track the progress of IT initiatives, monitor performance and measure results against IT goals. |
Adobe Workfront | A work management software that allows organizations to plan, execute, and track their work in real-time. It can also be used for strategic planning, enabling IT leaders to define and roll out efficient IT strategies . |
Monday.com | A work management software that allows teams to plan, execute, and track their work in real-time. It also has strategic planning features, including templates.. |
Workboard | Workboard is actually a strategy execution platform that you can use to plan, execute, and track your IT strategy while aligning Objectives and Key Results ( OKRs) in real-time. |
Also Read: Types of small business software
IT strategic plan best practices
These best practices provide a foundation for creating a strategic plan that will surely make the difference between success and failure. It is about creating a plan that will not only help you navigate through the present but also be ready for the future.
- Involve key stakeholders: It's important to involve key stakeholders from various departments. This is the best way to identify the specific needs of different groups, and ensure that the final strategy addresses those needs effectively.
- Understand the organization's digital maturity: Digital maturity is a measure of how well an organization has adopted digital technologies. A more mature organization is able to take full advantage of digital technologies, whereas a less mature organization may struggle to make effective use of them. It's important to have a clear understanding of the current digital maturity level. This includes assessing the current state of IT systems, as well as identifying areas for improvement.
- Understand the role of emerging technologies: Emerging technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, machine learning, and blockchain have the potential to disrupt traditional business models, create new opportunities, and improve organizational performance. Make sure that the plan contains a clear roadmap on how to constantly keep a close eye on these technologies and their potential impact on your industry.
- Develop a clear governance structure: The plan should include a governance structure that outlines responsibilities and decision-making processes related to IT.
- Assess IT costs vs. value: IT can be a significant expense, and the strategic plan should provide for accurate assessment of the costs vs the value of IT investments. A key aspect of this is understanding the total cost of ownership (TCO) of IT investments, which includes not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and other costs.
Conclusion
For optimal success, the IT strategic plan must be monitored, evaluated and revised regularly. This is the only way to guarantee that it remains pertinent and in line not only with the organization's objectives but also with the contemporary tech environment.
Do not be too fixated though on the need to have the perfect IT strategy plan from the start. Instead, approach the process with agility. Prioritize creating a minimal but functional plan, understanding that you will continue to refine and enhance it as you go.
FAQ Section
What is an IT strategy planning process?
The IT strategic planning process refers to the methodical approach that organizations use to align their information technology (IT) capabilities with their overall business goals and objectives. The goal of the process is to ensure that the organization's IT investments are aligned with its overall strategy and are helping to drive business growth.
Please don't confuse this process with the project planning process, which is used to assign tasks to different projects. Strategy mapping on the other hand helps you determine your mission, vision, and goals. These terms are often confused, but they mean different things.
What is the role of a strategic IT plan?
The primary role of an IT strategic plan is to align the organization's IT capabilities with its overall business strategy and to help drive business growth.
The plan identifies specific IT projects and initiatives that need to be undertaken. It helps the organization prioritize these initiatives, allocate resources, such as budget and personnel, improve its IT capabilities by identifying areas where improvements are needed, and ensure that IT is being used efficiently to support the organization's business goals. It also facilitates communication and coordination across the organization by providing a common understanding of the IT goals, objectives and initiatives.
Why is strategic planning important for IT professionals?
Strategic planning is important for IT professionals for these reasons:
- Understanding needs: Strategic planning can help IT professionals to better understand the organization's needs and priorities, and position themselves as valuable contributors to achieving the organization's goals.
- Resource allocation: By participating in the strategic planning process, IT professionals can help the organization prioritize its IT investments by identifying the projects and initiatives that are most critical to the organization's success. This ensures that resources are being allocated to the areas that will have the greatest impact.
- Efficiency: Strategic planning can help IT professionals ensure that IT is being used efficiently.
- Building relationships and trust: Strategic planning allows IT professionals to collaborate with other departments, stakeholders and key decision makers. This can help build trust and collaboration across the organization.
- Managing change: IT Strategic planning allows IT professionals to anticipate and manage change, helping them to be proactive and responsive to changes, rather than reactive.
IT Strategic Planning FAQ
What is IT Strategy?
IT strategy is an extensive plan that can help companies understand how to use technologies to meet their business and IT goals. It refers to a written document that points out various factors that can affect a company's use of technology.
What is IT strategic planning?
IT strategic planning involves creating a detailed blueprint that outlines how technology investments will support the organization's business objectives. This plan should encompass everything from resource allocation to project timelines.
How does an organization benefit from IT strategic planning?
Effective IT strategic planning aligns technology initiatives with business goals, which can lead to improved efficiency, increased productivity, cost savings, and a competitive advantage. It can also help manage risks and identify opportunities for innovation.
What are the key components of an IT strategic plan?
An IT strategic plan generally includes the following components: business objectives and strategies, IT objectives and strategies, a technology roadmap, a resource allocation plan, a risk management plan, and a governance model.
How often should an IT strategic plan be updated?
An IT strategic plan should be reviewed and updated regularly, usually on an annual basis. However, the plan should also be flexible enough to accommodate any unexpected changes or opportunities that may arise.
What role do emerging technologies play in IT strategic planning?
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things have the potential to disrupt traditional business models and create new opportunities. An IT strategic plan should therefore include a roadmap for monitoring these technologies and assessing their potential impact on the organization.
What is an IT strategic planning process?
IT strategic planning process refers to the method that organizations use to develop plans to achieve overall goals. The project planning process, on the other hand, is used to assign tasks to different projects.
What is a roadmap in IT?
A roadmap in IT is a document or visual representation that outlines the planned initiatives, projects and activities that an organization will undertake to achieve its IT goals and objectives over a specified period of time. A roadmap typically includes a high-level overview of the initiatives and projects that are planned, along with more detailed information such as timelines, milestones, and dependencies.
How does IT strategic planning support digital transformation?
Digital transformation is the process of using digital technologies to create new or modify existing business processes, culture, and customer experiences. An IT strategic plan can help an organization identify the key areas that need to be transformed, prioritize digital transformation initiatives, and plan the implementation of the necessary technologies.